In the architectural lexicon of windows, few designs manage to blend seamless functionality, robust durability, and sleek modern aesthetics as effectively as the aluminium sliding window. A ubiquitous feature in contemporary homes, commercial spaces, and high-rise apartments, these windows have evolved from simple utilitarian openings to sophisticated building components that significantly impact a structure’s performance, comfort, and character. This in-depth exploration delves into the world of aluminium sliding windows, examining their construction, benefits, types, applications, and the considerations for choosing the perfect system for any project.
1. Defining the Aluminium Sliding Window
An aluminium sliding window is a type of window that opens horizontally on a track system, rather than swinging inward or outward on hinges. The fundamental principle involves two or more sashes (the frames that hold the glass) that glide past one another. Typically, one sash is fixed in place, while the other is operational, sliding open to create a ventilation aperture. The entire structure—the sashes and the fixed frame that houses them—is fabricated from extruded aluminium profiles.
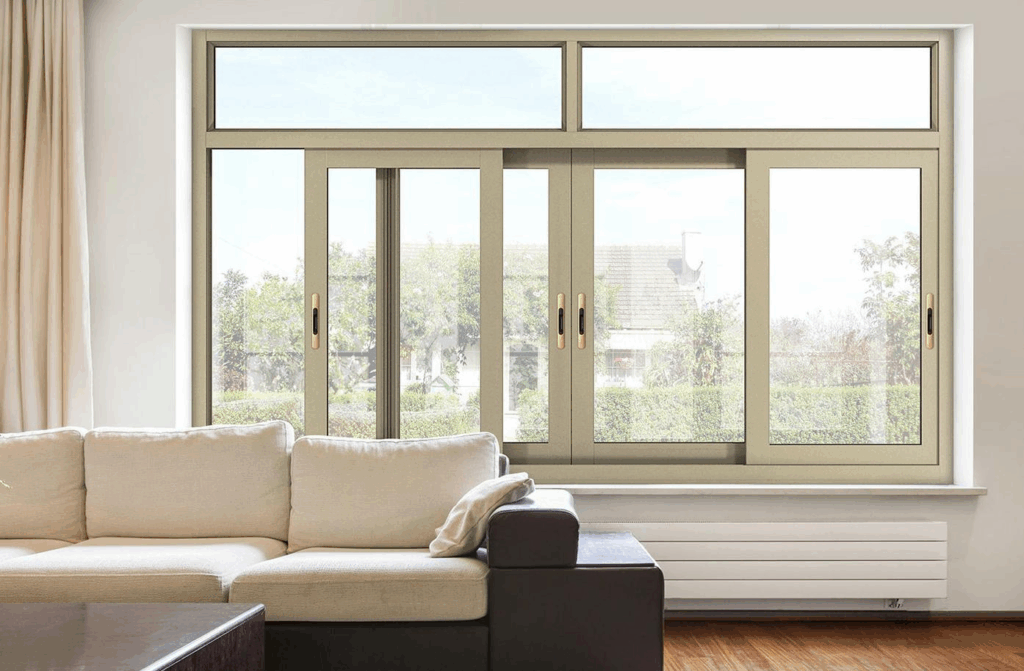

This simple yet effective mechanism is the cornerstone of its appeal. The use of aluminium as the primary material is not arbitrary; it is a deliberate choice that imparts a set of inherent advantages, making these windows a preferred solution for a wide range of architectural styles, from minimalist urban dwellings to sprawling commercial complexes.
2. Anatomy and Construction: How They Are Made
The strength and performance of an aluminium sliding window lie in its precise engineering and manufacturing process.

- Extrusion: The journey begins with the extrusion of aluminium billets. Heated aluminium is forced through a custom-shaped die to create long, continuous profiles that form the window’s frame, sashes, and other components. This process allows for the creation of complex, multi-chambered profiles that are crucial for thermal and structural performance.
- Thermal Break: In high-performance systems, a critical feature is the “thermal break.” This is a polyamide bar that is mechanically locked into the aluminium profile during extrusion. It effectively separates the interior and exterior halves of the window, creating a barrier that drastically reduces heat transfer. This prevents the interior aluminium from becoming cold in winter and hot in summer, thereby improving energy efficiency and eliminating condensation.
- Glazing: Modern aluminium windows are almost exclusively glazed with insulating glass units (IGUs). An IGU consists of two or more panes of glass separated by a spacer and sealed to create a hermetically closed air or gas-filled space. The gaps are often filled with inert gases like Argon or Krypton, which offer superior insulating properties compared to air. Further enhancements include Low-Emissivity (Low-E) coatings—microscopically thin, virtually invisible metal or metallic oxide layers on the glass that reflect infrared heat (keeping heat inside in winter and outside in summer) while allowing visible light to pass through.
- Hardware and Seals: The sliding mechanism is supported by high-quality hardware, including precision-engineered rollers and tracking systems made from stainless steel or durable composites. Multiple layers of EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) rubber seals are integrated into the frame and sashes to ensure an airtight and watertight seal when the window is closed, protecting against drafts, rain, and noise infiltration.
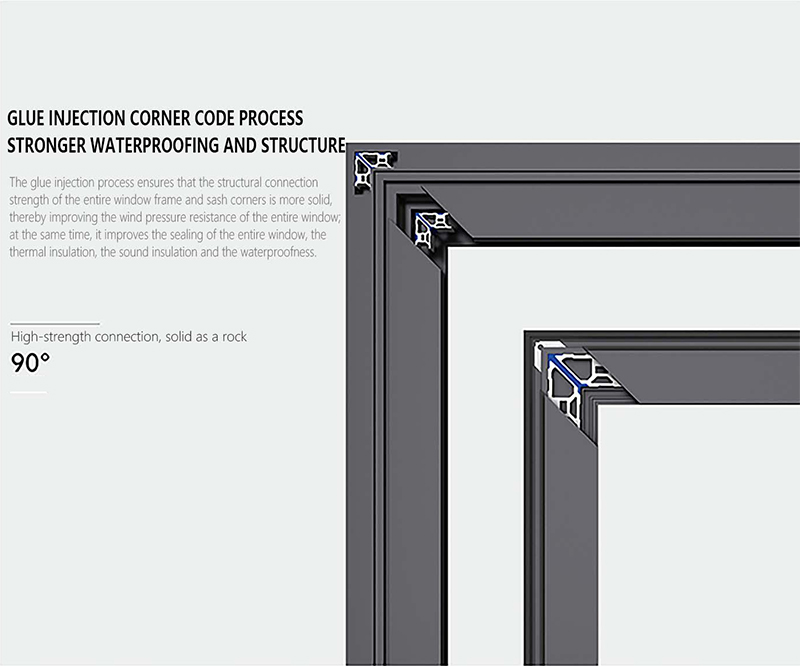
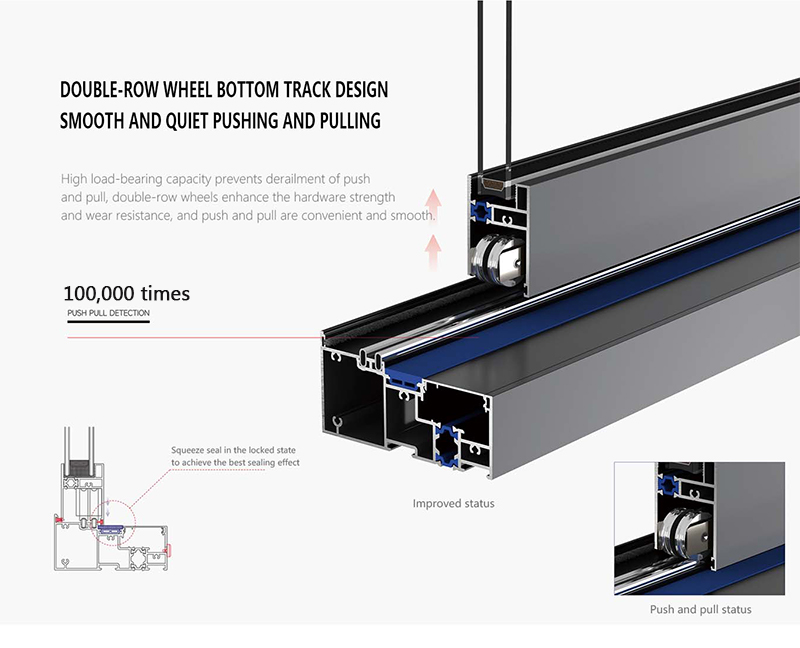

3. The Compelling Advantages: Why Choose Aluminium Sliding Windows?
The popularity of aluminium sliding windows is rooted in a powerful combination of practical and aesthetic benefits.
A. Unmatched Durability and Low Maintenance:
Aluminium is inherently strong and robust. Unlike timber, it does not warp, rot, or succumb to pest infestation. It is also highly resistant to corrosion. Modern architectural aluminium is treated with a pre-treatment and then finished with a powder coating, a durable, baked-on finish that is available in a virtually limitless range of colours (from classic whites and blacks to vibrant custom shades) and textures (e.g., matte, metallic, woodgrain). This finish is highly resistant to chipping, fading, and weathering, meaning these windows require minimal maintenance—an occasional wipe-down with soapy water is typically all that’s needed to keep them looking new for decades.
B. Strength for Structural Integrity and Large Spans:
The high strength-to-weight ratio of aluminium is a game-changer for window design. It allows for the creation of remarkably slender sightlines (the visible width of the frame). This means less obtrusive framing and more glass area, which translates to maximised natural light and unobstructed views. Furthermore, this inherent strength enables the fabrication of very large window panels that would be impractical or impossible with materials like uPVC or timber, making them ideal for creating dramatic floor-to-ceiling glass walls or large panoramic openings.
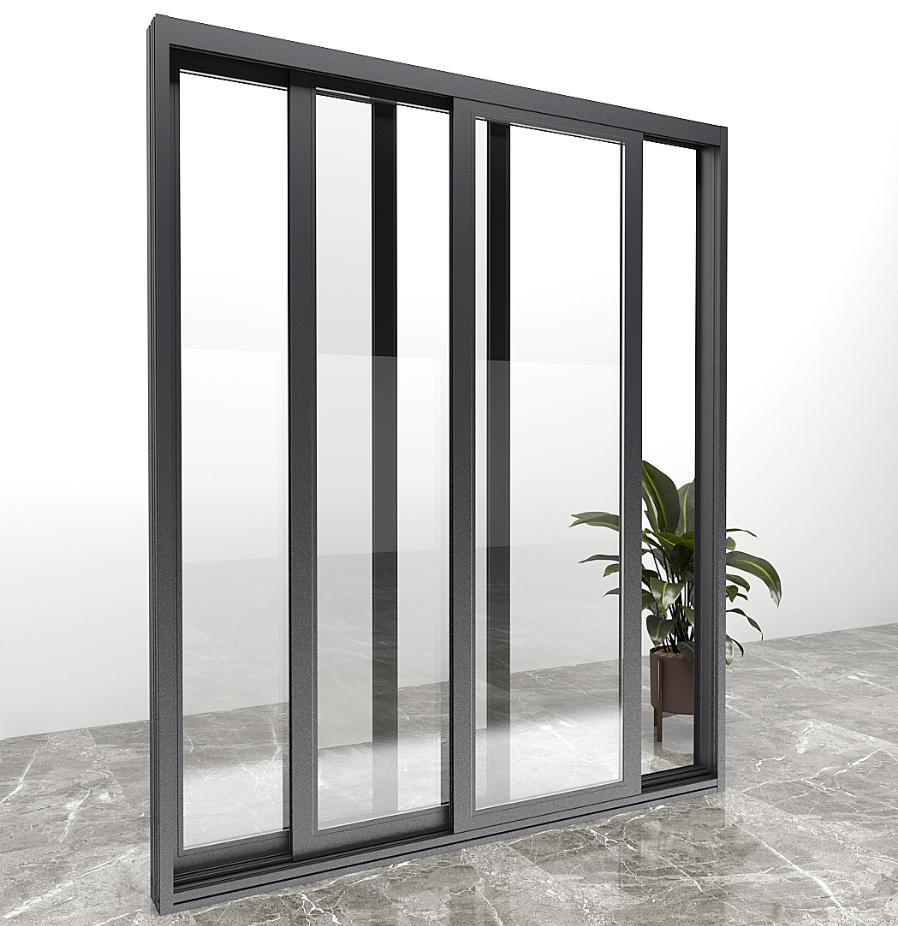

C. Sleek, Modern Aesthetics and Design Versatility:
Aluminium sliding windows are synonymous with clean lines and a minimalist aesthetic that complements modern architecture. The slim profiles contribute to a light and airy feel, both inside and out. Their design versatility extends beyond colour; they can be configured in various grid patterns, and the frames can even be clad with real wood veneers on the interior to achieve a traditional look while retaining all the external benefits of aluminium.
D. Superior Energy Efficiency and Weather Performance:
Contrary to the outdated belief that metal windows are poor insulators, thermally broken aluminium sliding windows are exceptionally energy efficient. The thermal break technology, combined with triple-glazed IGUs filled with argon gas and Low-E coatings, can achieve outstanding U-values (a measure of heat loss), rivaling and often surpassing other window materials. When coupled with robust sealing systems, they create a highly comfortable indoor environment, free from drafts and cold spots, while significantly reducing heating and cooling costs.
E. Effortless Operation and Space Efficiency:
The sliding mechanism is intuitively easy to use. The sashes glide smoothly along the track with minimal effort. Most critically, because they do not swing inward or outward, they are the perfect solution for spaces where conservation of floor and wall space is paramount. They can be placed in tight corridors, above kitchen sinks, or in rooms where furniture placement would be obstructed by a casement or awning window.

F. Environmental Sustainability:
Aluminium is a highly sustainable material. It is 100% recyclable without any loss of its inherent qualities, and the recycling process requires only 5% of the energy used to produce primary aluminium. Choosing aluminium windows made with a high recycled content contributes to a building’s overall green credentials and supports a circular economy.
4. Common Types and Configurations
While the basic sliding principle remains the same, several configurations are available:
- Two-Panel Slider: The most common type, featuring one fixed sash and one operating sash that slides horizontally.
- Three-Panel Slider (Centre Glide): Features two operating sashes that slide from the centre towards the sides, meeting in the middle when closed. This allows for a much wider opening, up to 50% of the total window width.
- Three-Panel Slider (One Operating): Has two fixed sashes on the sides and one operating sash in the centre that slides over either of the fixed panels.
- Lift-and-Slide Doors: While technically a door system, these operate on the same principle but on a larger, more robust scale, allowing for vast, seamless openings between interior and exterior spaces.
5. Applications: Where They Shine

Aluminium sliding windows are incredibly versatile:
- Residential: Perfect for modern homes, balconies, rear extensions, and rooms with stunning views.
- Commercial: Widely used in office buildings, retail stores, and schools due to their durability, low maintenance, and clean appearance.
- High-Rise Buildings: Their strength, light weight, and ability to withstand high wind pressures make them the default choice for skyscrapers.
6. Considerations and Potential Drawbacks
No product is without its considerations. The primary drawback of high-quality, thermally broken aluminium windows is their initial cost, which is often higher than uPVC or basic aluminium systems. However, this is an investment that pays dividends in longevity, performance, and energy savings. Cheaper, non-thermally broken versions should be avoided in climates with temperature extremes, as they will perform poorly. The tracks, if not properly maintained, can accumulate dirt and debris, potentially hindering smooth operation, though modern systems often feature raised tracks and drainage weeps to mitigate this.
Conclusion
The aluminium sliding window is far more than a simple portal to the outside world. It is a testament to material science and engineering innovation, offering a harmonious blend of form and function. Its enduring strength, minimalist elegance, exceptional energy performance, and practical operation make it a compelling choice for anyone seeking to enhance their living or working environment. By understanding its features and benefits, homeowners, architects, and builders can make an informed decision, selecting a window system that will provide beauty, comfort, and reliability for a lifetime.